The chassis number or Vin Number is a unique alphanumeric identification code that allows vehicle manufacturers to identify units produced throughout the world. Consisting of 17 digits, it is like a fingerprint that makes it impossible to mark another frame with the same number. This code is crucial not only for vehicle registration, but also for warranties, theft tracking and identification with insurance companies.
Before 1981, there was no single standard for VIN numbers, which made it difficult and sometimes impossible to verify the vehicle’s history through the VIN number.
Laser marking is fundamental because it guarantees the precision and reliability of the engraved information, as well as durability over time. Furthermore, it allows you to mark alphanumeric codes on different thicknesses and materials quickly and efficiently.
In conclusion, the Vin Number is a unique identification code essential for registration, warranties, theft monitoring and identification with vehicle insurance companies. Laser marking is the best technology to mark this code in a precise, reliable and long-lasting way.
How to read the VIN number?
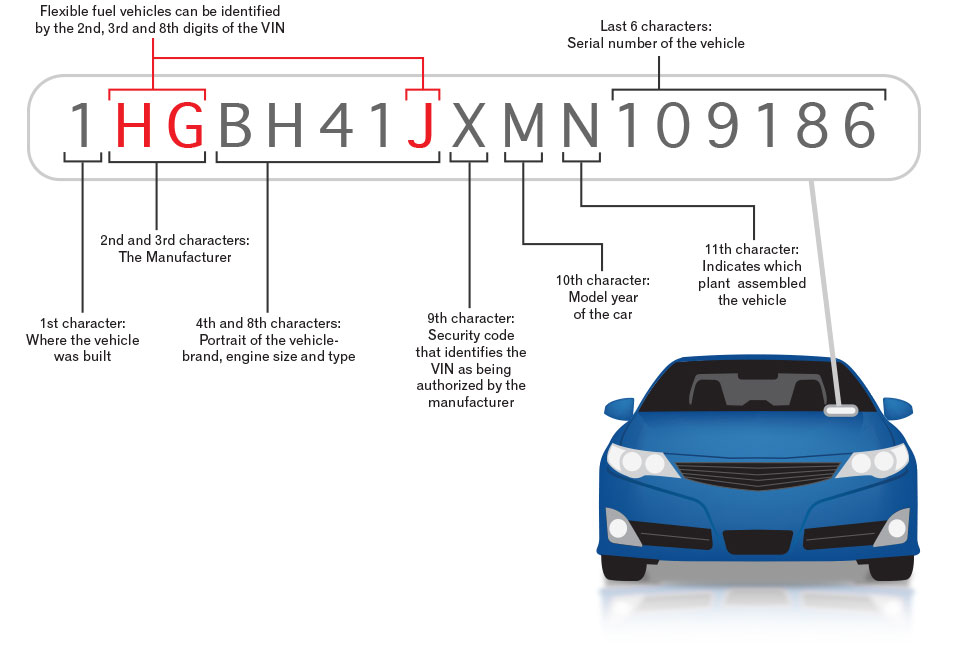
The VIN number is a unique code made up of 17 alphanumeric characters, made up of letters and numbers. However, letters such as “O” and “I” are not used as they could be confused with the numbers “0” or “1”. Each number is unique and assigned to a specific vehicle, making future identification very easy. To understand how to read the VIN number, it is important to know that it is divided into three parts.
The first part is called WMI (World Manufacturer Identifier), which consists of the first three characters and identifies the international symbol of the car manufacturer. This code is assigned by the competent office of the country and in accordance with the agreement with the ISO standardization organization or its national representative.
The second part is called VDS (Vehicle Descriptor Section), which consists of 5 or 6 characters and provides technical information and characteristics of the vehicle and are coded by the manufacturers themselves.
The third part is called VIS (Vehicle Identifier Section), which consists of the vehicle’s serial number. It is made up of eight characters, counting from the end of the VIN. It provides information such as the year of production and place of assembly of the vehicle, as well as the serial number of the series.
In summary, WMI+VDS+VIS make up the VIN chassis number, always made up of 17 characters and each of the three parts describes specific information about the vehicle.
Additionally, it is important to note that the VIN number is assigned to the vehicle during manufacturing and cannot be changed later. This means that the VIN number will remain the same throughout the life of the vehicle, making it easy to trace its history and verify its authenticity.
The VIN number is usually engraved on the vehicle’s chassis and registration document, but can also be found on other parts of the vehicle such as the dashboard or door pillar. In the event of theft or loss, it is important to report the VIN number to the competent authorities to facilitate the search for the vehicle.
In conclusion, the VIN number is a unique code assigned to the vehicle by the manufacturer, composed of 17 alphanumeric characters and divided into three parts. It serves as vehicle identification and can be used to verify vehicle history, registration, warranties and theft prevention. Engraved on the vehicle chassis, on the registration document, and in some cases on other parts of the vehicle, it is an essential element for the safety and traceability of the vehicle.